Guest Blog: Business @ speed of thought: The power of 5G, Edge, and IoT
5G is the next frontier in mobile connectivity. With its reduced latency, faster data speeds, and 24x7x365 connectivity, it holds immense promise for businesses and individuals, empowering them to accomplish work at a pace hitherto unimaginable. Some experts believe that 5G will completely replace the super-fast broadband connections, further enabling the exponential growth in IoT-enabled devices that require faster and more reliable computing power. Edge Computing promises to process nearer to the source of data, bringing the cloud’s ability closer to home and increasing device responsiveness.
This Point of View paper explores the advantages of 5G and discusses how in tandem with edge computing, cloud, and IoT, will revolutionize work and life as we know it today.
The advent of 5G and its benefits
The 4G technology didn’t just resolve bandwidth issues; it revolutionized the way people consume information, collaborate, and perform at work. However, the technology is not without its limitations:
- Subscriber devices need to match frequency bands and settings for the local carrier or country, which is an issue when people travel.
- Network and software updates are routinely required to maintain service levels.
- Users tend to experience short battery life on their phones with 4G, compared to 3G.
- Most importantly, with the advent of IoT and new age technologies, 4G cannot support the bandwidth required by organizations and individuals, to achieve enhanced connectivity and speed.
With the 5G revolution upon us, the telecom industry, comprising mobile device manufacturers, network service providers, and businesses alike, are gearing up to embrace the transformation. A recent study by Nokia states that nearly half – 47% of the organizations that participated in the survey have begun to plan for 5G adoption1. Let us look at some of the advantages of 5G for businesses (Refer Table 1):
|
|
4G Connectivity |
5G Connectivity |
|
Latency |
70ms (average) |
1ms |
|
Download speed (average) |
1 gbps |
10gbps |
|
Potential cell density |
300-400 users per cell (average) |
100x of 4G |
|
OFDM encoding |
20 MHz channels |
500-800 MHz channels |
Table 1: Differences between 4G and 5G networks
Faster data speeds
5G networks are potentially 100 times faster than 4G at the promised potential of 10 gigabits per second (Refer Figure 1) – an alternative to broadband connections.
Greater capacity
5G promises to deliver up to 1000x more capacity than 4G, enabling a more robust connection across devices and networks in the IoT-enabled world, characterized by cloud computing. This will allow employees and organizations to stay connected anywhere, anytime, and accomplish work incredibly efficiently.
Increased bandwidth
5G networks support greater optimization of network bandwidth - a boon for enterprises processing massive volumes of data by the second into actionable information.
Reduced latency
5G dramatically reduces latency, the time taken for a signal to pass from the source to the receiver and then back again, enabling organizations to leverage the power of IoT truly.
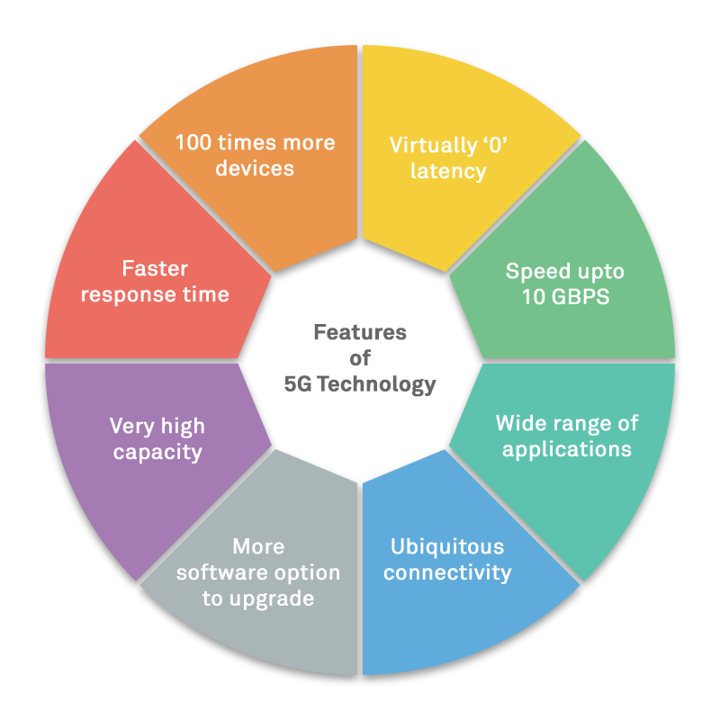
Figure 1: Advantages of 5G
Edge computing with 5G
Edge computing is gaining traction as enterprises leverage distributed computing power to bring processing and data storage closer to the physical location. Next-gen technologies, including the internet of things (IoT), cloud computing, and software-defined networking (SDN), require vast volumes of data to be transmitted, analyzed, and processed in real-time. The advent of 5G promises to provide a fillip to cloud computing, helping organizations harness edge computing power with real-time connectivity across the spectrum of devices and the cloud. Future computing resources will be widely distributed across the networking landscape, with edge computing complementing centralized cloud computing environments.
Edge computing brings the power of a supercomputer to every device. Moving workloads from devices into the cloud, edge computing optimizes latency and reliability issues – two of cloud computing’s most significant limitations. At the same time, it facilitates substantial savings in processing resources by placing application components close to the devices. As a result, critical data is processed on the “edge” at lightning speed, while secondary data is processed on the cloud.
As 5G and edge grows in popularity, the industry is divided in its opinion on cloud computing’s future. Some experts argue that edge heralds the beginning of the end of cloud computing as we know it. However, the reality is likely that most forward-looking organizations will leverage the combined powers of edge computing and the public cloud to optimize and amplify their computing power and resources. 5G technologies facilitate increased network capacity and reduced latency, enabling public cloud service providers to offer fast delivery to enterprise mobile customers across a wide range of IoT-enabled devices. 5G will expand the cloud storage capacity for big data and support storage and data retrieval from the cloud at breakneck speeds. It will also enable faster machine-to-machine communication and lead to mobile cloud services’ growth, helping enterprise workers easily access virtual machines via their phones. 5G will also enable faster hotspots, giving remote workers reliable access to cloud services even with limited or poor internet connectivity.
This can transform how government organizations, large-scale enterprises, and large sectors, including healthcare and the education segment, operate. In developing nations like India, 5G can facilitate the growth of cloud computing services in rural areas that have previously had poor or zero access to high-speed internet. 5G can also facilitate large-scale adoption of IoT across industries, supporting a vast array of connected devices across a wide range.
The emergence of 5G along edge and cloud computing will result in superior capacity and flexibility, leading to the next generation of highly competitive IoT and cloud services, reducing costs, and boosting innovation.
Leverage the power of 5G, edge, and cloud
5G and edge computing can provide better control over data, faster processing and analysis, and seamless operational agility. Unified communications services used across organizations will benefit from 5G’s improved speed and service reliability. Here are three use cases of how 5G, together with IoT, edge computing, and cloud, can transform the landscape for organizations of the future:
Transformed healthcare
The adoption of 5G, cloud, and IoT has revolutionized healthcare during the pandemic. With patients hesitant to visit the hospital for fear of exposure to infection, 5G and IoT together enable remote monitoring and tracking of a patient’s health through various IoT enabled wearables and connected devices. Doctors can assess a patient’s health condition virtually and leverage the cloud to instantaneously analyze historical data on similar situations to determine the best course of treatment for the patient. What’s more, if the patient’s health records over the last 3-5 years are available on the cloud, the doctor can study the patient’s history to offer a more holistic diagnosis. 5G applications include:
- Enabling the transmission of heavy diagnostic files like PET and MRI scans in split seconds to the remotest areas
- Improving the use of AR and VR in healthcare for both simulated studies and improved patient engagement
- Supporting telemedicine and virtual consultation in remote, far-flung areas to provide healthcare access to millions who have hitherto been denied the basic services
Pivotal role in Insurance
5G, IoT, and cloud have revolutionized the automobile and insurance segments. Automobile owners typically pay insurance premiums based on the age and value of the vehicle. However, it is not uncommon to find cases where the car is relatively new, but the premium is rather high. This is because insurance provision is linked to the driver’s license and driving history based on data and traffic violations logged against the license.
This has now been taken a step further with insurance providers in the US and other developed countries installing sensors in the car to study and determine driving patterns, including braking, speed, and acceleration in relation to other vehicles around them. All of this data is transmitted via IoT to the cloud, processed in batches, and analyzed thoroughly by insurance providers before determining the insurance amount.
Immersive retail experiences
A Gartner study revealed that by 2020, 100 million consumers would be using augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for both online and in-store shopping.2 Adoption of AR and VR has been slow in retail despite all the hype and excitement. This is primarily due to connectivity and speed issues, as these devices need to access and process vast volumes of data on the fly. 5G, with IoT and edge, will revolutionize the mixed reality market, enabling these technologies to become mainstream, taking retail experiences to the next level. IoT-based facial recognition supported by 5G speed will provide retailers with the shoppers’ demographics and sentiments enabling a hyper customized shopping experience including real-time price and product updates. The combination of technologies also supports different payment systems with wearables and can eliminate lengthy queues at point-of-sale (PoS) terminals.
5G enabled computing: the next frontier
Imagine a world where there is no need for cables and wires to deliver communication or entertainment content to your devices at work and home. This will be the reality soon as network service providers across the globe prepare to embrace 5G.
5G and edge computing, combined with the cloud’s computational power, will improve response time, save bandwidth, and push processing and analyzing power and capabilities to the next frontier. Together, they have the potential to unleash an unmatched computing and communication power across the enterprise world, transforming the very nature of business operations across verticals.
Guest blog by Rajiv Kumar, GM & Presales Head - Cloud, Cloud & Infrastructure Services, Wipro.
Rajiv has about 22 years of experience in the IT Industry. He has played a crucial role in developing next-generation transformative offerings like Azure Stack and rapidly growing the cloud practice across geographies. He is a member of the Association of Enterprise Architects and has many leading certifications like TOGAF, Azure MCSD, and AWS Solution Architect.
You can reach him at [email protected]
This insight was originally published on the Wipro website.


